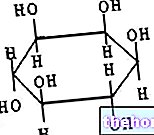
Being a precursor of NAD and NADP, it has mainly a coenzyme function in numerous processes.
Niacin is available both in foods of animal and vegetable origin, and can be obtained by endogenous synthesis only from the essential amino acid tryptophan. The recommended ration is about 6.6 mg per 1000 kcal taken with the diet.
The lack of nicotinic acid can trigger pellagra, while the excess - obtainable only at the pharmacological level - can cause side effects but to a lesser extent than nicotinamide.
Supplementing with niacin may be necessary to fill a nutritional deficiency or even to try to reduce cholesterol - if cholesterol-lowering drugs are not taken.
For further information: Vitamin PP - Vitamin B3 PP or B3, was identified as nicotinic acid (pyridyl-β-carboxylic acid) in 1937, during some studies on alcoholic fermentation.
The term niacin also refers to the respective derivatives, which have biological activity similar or similar to nicotinamide.
Nicotinic acid is found mainly in plants and nicotinamide is instead typical of animal tissues.
The biologically active forms of niacin are nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP) which act as coenzymes in numerous biological processes.
of the intestinal mucosa releasing niacin.At low concentrations, the absorption of niacin occurs by Na-dependent facilitated diffusion, while at high concentrations passive diffusion prevails.
All tissues are able to synthesize the coenzyme forms NAD and NADP starting from the niacin carried by the blood and transferred to the cells by facilitated diffusion.
90% of the niacin taken with food is methylated in the liver and eliminated by the kidneys; for this reason, the determination of methylated metabolites in the urine is used to evaluate the state of nutrition - in the urine of the adult in normal conditions there are 4 ÷ 6 mg / day.
carbohydrates, fatty acids and amino acids; NAD and NADP act as electron acceptors.
Despite the remarkable similarities of structure and mechanism of action, NAD and NADP perform quite different metabolic actions and many enzymes require one or the other.
- NAD mainly participates in the reactions that release energy (glycolysis, lipolysis, Krebs cycle) and becomes NADH which in turn transfers H (hydrogen ions) to the respiratory chain for the production of ATP;
- NADPH serves as a donor of H in biosynthesis reactions (fatty acids and steroids) and in the pentose phosphate pathway.
The preclinical phase of pellagra is characterized by nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, loss of appetite, weight loss, dizziness, headache and digestive difficulties. The overt deficiency manifests itself with skin (dermatitis), intestinal (diarrhea) and nervous (dementia) alterations, but the symptoms are extremely variable from individual to individual.
Generally, dermatitis is symmetrical and affects the parts of the body exposed to the sun with the appearance of erythematous and edematous skin areas (face, neck, wrists, back of hands, feet) which evolve into hyperkeratosis, hyperpigmentation, cracking and desquamation.
At the level of the digestive system there are lesions affecting the oral mucosa and tongue (glossitis) which appears dry, reddened at the apex and at the edges and sometimes de-epithelialized becoming scarlet red.
Early neurological symptoms include anxiety, depression and fatigue which can progress to severe depression, apathy, headaches, dizziness, irritability and tremors; if not treated they give rise to a real dementia with hallucinations, delirium and confusional state.
Two congenital diseases characterized by inadequate metabolic utilization of niacin are also known: Hartnup's disease and schizophrenia.
, nausea, vomiting and sometimes liver damage (2 ÷ 6 g / day). Doses of 1 g / day can cause intestinal damage and, in experimental animals, phosphaturia due to an increase in the concentration of NAD in the renal cortex and in the activity of hepatic microsomal enzymes.
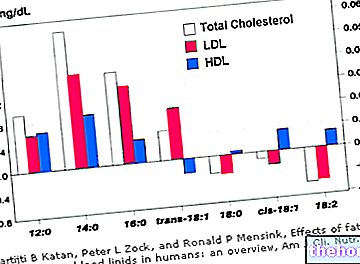
It has been seen that the administration of niacin in high doses reduces the levels of plasma cholesterol and triglycerides in the body: 1.5 ÷ 3 g / day of nicotinic acid reduce the levels of total cholesterol, LDL and increase HDL concentrations .
, especially wholemeal, legumes, meats, eggs, fishery products and offal.C "it should be emphasized that, in various foods, niacin is present in an unavailable form. Certain foods or drinks such as coffee contain it as a methylated derivative (trigonellin) unavailable to animals, but thermolabile, therefore transformable into nicotinic acid during roasting. In cereals it can be linked to polysaccharides, peptides or glycopeptides, in turn linked to cellulose or hemicelluloses which make it difficult to release; in corn it is covalently linked to small peptides (niacinogens) and glucides (niacitin), for which it becomes available only after treatment in a basic environment (the niacin contained in tortillas, unlike that present in polenta, is absorbable by the body).
Let's not forget that niacin can be synthesized in the body from the amino acid tryptophan. This is mainly present in protein foods such as eggs, cheeses, fish and meat, in which it generally ranges from 150 to 250 mg / 100 g of food (see: amino acid profile of foods).
an increase of 1 and 3 mg / day is expected, respectively.

.jpg)