Definition
Among the forms of anemia, the one commonly defined as "iron deficiency" is widespread, especially among infants, adolescents and women of childbearing age. Iron deficiency anemia is diagnosed when dietary iron is deficient in the blood; this deficiency derives from a reduction in both the intake and absorption of this important mineral.
Causes
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when iron levels in the body are so low that they are insufficient to produce enough hemoglobin, which is useful for transporting oxygen into the tissues. Iron deficiency anemia can be favored by several elements: iron deficient diet, haemorrhages, pregnancy, inability to absorb iron (typical consequence of celiac disease, steatorrhea, chronic diarrhea and gastric surgery), abundant menstruation.
Symptoms
Generally, iron deficiency anemia does not begin with any symptoms; as the disease progresses, the prodromes tend to manifest themselves more intensely, to the point of creating quite serious consequences: mood alteration, asthenia, increased heartbeat, tingling in the limbs , loss of appetite, inflammation of the tongue, intestinal malabsorption, headache, cold hands and feet, splenomegaly, brittle nails, dizziness.
Diet and Nutrition
The information on iron deficiency anemia - drugs for the treatment of "iron deficiency anemia is not intended to replace the direct relationship between health professional and patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking iron deficiency anemia - drugs for the treatment of" Iron deficiency anemia.
Medicines
The therapy aimed at the treatment of "iron deficiency anemia is called" martial "and is essentially based on the administration of ferrous salts, generally orally; in some cases, especially in patients who present malabsorption in the context of" iron deficiency anemia, it is preferable to take iron salts parenterally (intramuscularly or intravenously).
If the patient is malnourished, too thin or overweight, the iron deficiency anemia could depend on an unregulated diet: in this case, the first therapeutic measure is represented by the correction of eating habits. If the patient suffering from iron deficiency anemia takes too much fluids during the day, it is advisable to reduce the intake.
The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against iron deficiency anemia, and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the most suitable active ingredient and dosage for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state health of the patient and his response to treatment:
Iron supplements: Typical side effects of iron supplements are digestive disorders and associated disorders, such as abdominal cramps, diarrhea and heartburn. In order to avoid these unpleasant inconveniences, it is recommended to start administration with a low dosage, which will be gradually increased during therapy. Furthermore, even if the administration on an empty stomach would be more effective for the absorption of the product, the supplement is generally taken together with the meal or immediately after its end, given the gastro-intestinal effects it can cause.
- Ferrous sulphate (eg Ferrograd): antianemic par excellence, ferrous sulphate is widely used in martial therapy (iron deficiency anemia). Typically, the drug is available in the form of controlled-release tablets with 595 mg of active. It is recommended to take 1 tablet a day, with water. The drug requires a prescription. To improve absorption, it is recommended to take the drug with vitamin C (eg with a glass of orange juice).
- Iron dextran (eg Iron ATI 100 solution for injection): indicatively, take 25-100 mg of active by intramuscular or intravenous route. Consult your doctor.
- Iron fumarate (eg. Organic Iron): start therapy for iron deficiency anemia with 325 mg of drug orally, once a day. Continue with maintenance therapy by taking 325 mg of active, three times a day. The posology it remains the same for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia associated with kidney disease; it is recommended that the patient be subjected to regular checks.
- Iron gluconate (eg Sidervim, Cromatonferro, Bioferal, Losferron): available in effervescent tablets and effervescent granules. The dosage of this drug for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia is similar to that of iron fumarate.
- Carbonyl iron (eg Icar): the dose for adults suffering from iron deficiency anemia is 50 mg of active, to be taken orally, three times a day.
- Iron saccharate (eg Ferrum Hausmann Orale, Venofer): available in vials for oral use, it is recommended to take the drug in case of iron deficiency anemia at a dose of 2-3 vials (each containing 40 mg of iron), after meals. The dose should be reduced to 1-2 vials per day for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in children. Alternatively, it is also possible to take the drug by slow intravenous injection (5 ml of solution contain 100 mg of active), lasting 2-5 minutes. Consult your doctor.
There are also multivitamin supplements, formulated with multiple vitamins and minerals: for example Multicentrum, Supradyn, Be-Total Plus.
Since iron supplements tend to cause constipation, it is possible to take laxatives, such as Glycerin (eg San Pellegrino Glycerin Suppositories), liquid paraffin, peanut oil. Do not abuse.
Hematopoietic growth factors (HGF): they are useful when iron deficiency anemia depends on renal insufficiency or neoplasms. Drugs (eg formulated with Erythropoietin: Eprex, Epoxitin), stimulating the synthesis of red blood cells, rebalance iron levels in the blood.
Blood transfusions: in particularly serious cases, in which iron deficiency anemia cannot be cured with the drugs listed above, it is possible to proceed with a blood transfusion.
Secondary therapies for the prevention of anemia and to treat secondary symptoms
If neither iron supplementation nor the correction of eating habits were sufficient to cure iron deficiency anemia, the patient must undergo more in-depth checks, in order to identify the real cause that triggers the iron deficiency in the blood. Depending on the etiological element, the doctor can prescribe antibiotics, oral contraceptives or recommend surgery:
1) Antibiotics: anemia could also be related to a peptic ulcer; therefore, the treatment of this disease could also balance the iron levels in the blood.
- Metronidazole (eg. Metronid, Deflamon): take one 250 mg tablet every 6 hours.
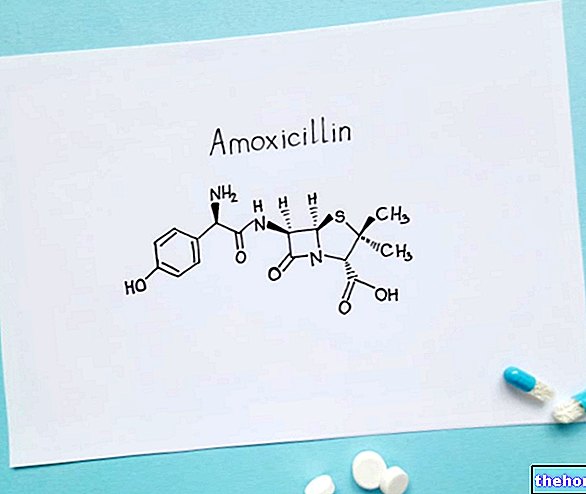
- Amoxicillin (eg Augmentin, Klavux) belongs to penicillins: it is a bactericide capable of inhibiting the synthesis of the cell wall of the bacteria (Helicobacter pylori), responsible for the peptic ulcer. Take one tablet orally (1 gram) 2-3 times a day for 14 days.
2) Oral contraceptives: in case of particularly heavy menstruation, the risk of iron deficiency anemia increases considerably, given the large amount of blood lost due to hypermenorrhea. Oral contraceptives, regulating menstrual flow, could represent a possible therapeutic option.
- Ethinylestradiol / Levonorgestrel (eg Loette, Microgynon, Miranova, Egogyn): these drugs are available in packs of 21-28 tablets: each tablet consists of 0.02 mg of ethinylestradiol and 0.1 mg of levonorgestrel. Pharmacological treatment involves taking one tablet a day, for 21 days, possibly at about the same time each day, followed by a free interval of one week.
- Desogestrel / Ethinylestradiol (eg Gracial, Novynette, Lucill, Dueva, Securgin): these are coated tablets of 20 mcg of ethnylestradiol and 150 mcg of desogestrel. The dosage of these drugs reflects the one described above: the correct way of taking these active ingredients generally guarantees a significant reduction in menstrual flow. It should not be forgotten, however, that in some patients worsening of the prodromes is sometimes observed: in In this case, do not hesitate to contact your doctor. In any case, in the first three months of taking the pill, a change in symptoms, either positive or negative, is very frequent.
3) Finally, among the causes responsible for "iron deficiency anemia there are also bleeding polyps, fibroids or tumors of the uterus: in this case, iron deficiency must be considered as a secondary symptom, useful for the diagnosis of the disease." The surgical removal of the bleeding polyp or the abnormal mass, in all probability cancels the iron deficiency anemia.
Other articles on "Iron deficiency Anemia - Drugs for the Treatment of" Iron deficiency Anemia "
- Anemia: symptoms, diagnosis, therapy
- Iron deficiency anemia