Definition
For laryngitis s "means any inflammatory process affecting the larynx and the vocal cords contained in it: by becoming inflamed, the vocal cords modulate their ability to vibrate, consequently altering the sound of the voice, which sometimes disappears completely.
Causes
Often times laryngitis is the most immediate consequence of a "viral infection; even the excessive use of the voice, the abuse of alcohol, smoking, drugs and chemicals, and gastroesophageal reflux, can certainly irritate the larynx and create Inflammation In severe cases, chronic laryngitis is a sign of laryngeal cancer.
Symptoms
Laryngitis begins with altered tone of voice, which becomes hoarse and hoarse, nasal congestion, sore throat (pharyngitis), runny nose and shrill and difficult breathing; sometimes, laryngitis is accompanied by other symptoms, such as difficulty in breathing. swallowing solid and liquid foods, dysphagia, fever, headache, tonsillitis and other typical flu symptoms.
Natural Cures
The information on Laryngitis - Medicines for the Treatment of Laryngitis is not intended to replace the direct relationship between the health professional and the patient. Always consult your doctor and / or specialist before taking Laryngitis - Medicines to Treat Laryngitis.
Medicines
Acute viral laryngitis tends to self-resolve, sometimes even without the use of specific drugs; for chronic forms of laryngitis, treatment is essentially based on treating the underlying causes (heartburn, alcohol or smoking abuse, etc.).
The following are the classes of drugs most used in the therapy against laryngitis and some examples of pharmacological specialties; it is up to the doctor to choose the most suitable active ingredient and dosage for the patient, based on the severity of the disease, the state of health of the patient and his response to treatment:
Antibiotics and antifungals
Only rarely are antibiotics used in therapy since, as analyzed, laryngitis depends most of the time on viruses: in any case, if laryngitis is related to bacteria (a rare event), antibiotics prove to be the therapy of choice. .
The choice of the drug must always be established by the doctor on the basis of the responsible bacterium; otherwise, it is recommended to take drugs with a broad spectrum of action. For example:
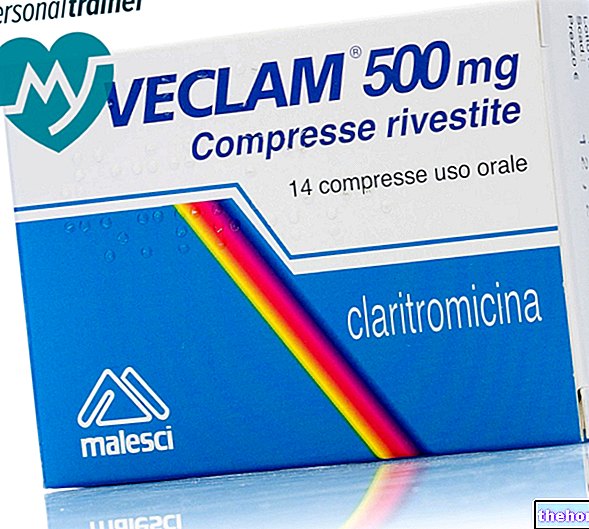
- Clarithromycin (eg. Biaxin, Macladin, Klacid, Soriclar, Veclam): take 250-500 mg of active every 12 hours. In case of Haemophilus influenzae infection, take 500 mg of the drug for 10 days.
- Telithromycin (eg Ketek) belonging to the class of macrolides, this drug is indicated both for the treatment of bacterial laryngitis and pharyngitis. Take one 400 mg tablet daily for 7-10 days.
For the same reason, antifungal drugs are used in laryngitis therapy when inflammation of the larynx is caused by a fungal attack.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids (eg Cortisone, prednisone), powerful anti-inflammatory drugs, are used in therapy for the treatment of laryngitis only in extreme, severe and complicated cases.
Antacid drugs
As we have analyzed, gastroesophageal reflux - also closely related to gastric heartburn - can favor or exacerbate laryngitis; for this purpose, it is possible to take specific drugs capable of reducing the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
Very useful, in this sense, are the PPIs (inhibitors of the proton pump), such as:
- Lansoprazole (eg. Lansox, Lomevel, Pergastid): the drug should be taken at a dosage of 15 mg (one tablet) once a day, before the main meal; in general, therapy should be continued for 4 weeks, as prescribed by the doctor.
- Omeprazole (eg. Antra, Nansen): start therapy by taking 20 mg of active substance (1 tablet) per day, for 4-8 weeks. As needed, increase the dosage to 40 mg / day.
The use of these drugs is essential for healing from reflux diseases; if laryngitis is closely related to these diseases, PPI therapy is particularly effective.
Therapeutic aids and behavioral therapy
Since there is no specific treatment for the treatment of laryngitis, it is possible to use some therapeutic aids, very useful to accelerate the patient's recovery and decrease the painful perception in the throat:
- Ibuprofen (eg. Brufen, Moment, Subitene): take orally a dose of active equal to 200-400 mg (tablets, effervescent sachets) every 4-6 hours, as needed. In some cases, the analgesic can also be taken intravenously at a dosage of 400-800 mg every 6 hours, as needed.
- Paracetamol (or acetaminophen, eg Tachipirina) indicated to reduce pain in the throat and to decrease fever in the context of laryngitis. Taken orally in the form of tablets, syrup, effervescent sachets, or suppositories, the drug is generally administered at a dosage of 325 - 650 mg every 4-6 hours for 6-8 consecutive days, to balance the body temperature.
The patient suffering from laryngitis is advised to practice "behavioral therapy", useful for speeding up the recovery of full health:
- gargling of warm salt water, to be repeated several times a day, are very useful for relieving the sore throat
- take large quantities of fluids, even if you are not thirsty
- it is advisable to rest the vocal cords, limiting the use of the voice, until the symptoms improve
- the use of a humidifier has proved to be very useful for the treatment of diseases affecting the respiratory tract: the humid air seems to exert a discreet expectorant effect, releasing the mucus from the lungs. The use of the humidifier is recommended in the context of pneumonia, tonsillitis, pharyngitis and laryngitis.
- Natural "drugs" such as arnica, echinacea, helichrysum, sage and dog rose are recommended to speed up the treatment of laryngitis.