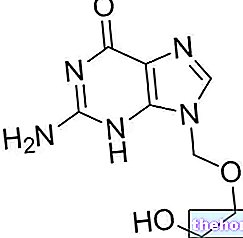
ASACOL ® is a mesalamine-based drug
THERAPEUTIC GROUP: Non-steroidal intestinal anti-inflammatory - Aminosalicylic acid and analogues

Indications ASACOL ® Mesalazine
ASACOL® is an intestinal anti-inflammatory drug, used in the treatment of intestinal inflammatory forms such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis.
The various formulations provided allow the treatment in the various stages of the disease.
Mechanism of action ASACOL ® Mesalazine
Mesalazine, contained in ASACOL ® is an anti-inflammatory belonging to the broadest category of aminosalicylic acids, with selective action against the intestinal mucosa.
This typical feature is essentially associated with the pharmacokinetic properties of the active ingredient, which taken orally in the form of gastro-resistant tablets, is able to pass the gastric acid barrier unscathed and be released at the ileal level, where it carries out its therapeutic action.
In fact, the topical anti-inflammatory action is possible thanks to the reduced rate of systemic absorption of mesalazine, which concentrating at the intestinal level, is able to inhibit the production of chemical mediators of inflammation such as the metabolites of arachidonic acid (prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes ) safeguarding the integrity of the intestinal mucosa.
While the active portion of the drug will subsequently be excreted through the faeces, the very small amount absorbed, following hepatic and intestinal acetylation, will be eliminated mainly through the urine.
Studies carried out and clinical efficacy
1. MESALAZINE IN ULCERATIVE COLITIS
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011
Randomized clinical trial: early assessment after 2 weeks of high-dose mesalazine for moderately active ulcerative colitis - new light on a familiar question.
Orchard TR, van der Geest SA, Travis SP.
Ulcerative colitis is one of those pathologies of the intestinal tract for which therapy with mesalamine is indicated. In this clinical trial it was noted that taking high doses of mesalamine for 2 weeks could provide rapid relief of the main symptoms of the disease, such as rectal bleeding and painful bowel movements, which lasted up to 6 weeks in most patients. treated.
2. MESALAZIN AND CHRONIC INFLAMMATORY PATHOLOGIES: THE STATE OF THE ART
Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 Mar 15.
Efficacy of 5-Aminosalicylates in Crohn's Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
Ford AC, Kane SV, Khan KJ, Achkar JP, Talley NJ, Marshall JK, Moayyedi P.
Despite the numerous studies that populate the international literature on the efficacy of mesalazine and other active ingredients belonging to the family of aminosalicylic acids in the treatment of intestinal inflammatory diseases, from a statistical point of view, it is not yet possible to formulate an unambiguous opinion. This evidence therefore , suggests the importance of starting new clinical trials, with numerous samples and standardized protocols, which can provide the clinician with an evaluation parameter.
3. MESALAZINE AND PREVENTION
Intern Emerg Med. 2011 Jan 29
Long-term treatment with mesalazine in patients with symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease.
Gatta L, Di Mario F, Curlo M, Vaira D, Pilotto A, Lucarini P, Lera M, Enkleda K, Franzé A, Scarpignato C.
Interesting Italian study that demonstrated how the cyclical intake of mesalazine for 10 days a month, in a clinical trial lasting 5 years, could reduce the incidence of diverticulitis in patients suffering from intestinal problems. This study, of little statistical value, however, assumes particular importance from the clinical point of view, given the preventive action of mesalazine.
Method of use and dosage
ASACOL ® 400/800 mg mesalamine gastro-resistant tablets or 400 mg mesalazine modified-release capsules: useful both in the treatment of active phases and in the prevention of relapses, it is recommended to take 1 - 2 tablets or capsules of 400 mg three times a day.
The intake should be preferred on an empty stomach, and under strict medical supervision.
ASACOL ® suppositories of 500 - 1000 mg of mesalazine : useful in the treatment of inflammatory affections localized to the rectal level, it is recommended to take a suppository of 1 g once a day or 2 - 3 suppositories of 500 mg a day.
In any case, in order for the drug to perform its maximum therapeutic action, the suppository must be held for long periods, such as at night.
ASACOL ® rectal foam of 1 - 2 - 4 gr of mesalazine and rectal suspension of 2 - 4 gr / 50ml: indicated in the treatment of rectal and sigmoid affections, it is recommended to take 1 dose of rectal foam or rectal suspension of 2 g, 1 or twice a day.
Intakes should preferably take place in the morning and before bedtime.
All the aforementioned dosages are purely indicative, as the doctor may vary the dosage and timing of intake based on the patient's clinical conditions.
Warnings ASACOL ® Mesalazine
Given the partial hepatic and renal metabolism of mesalazine, the intake of ASACOL ® should take place with particular attention and under strict medical supervision in patients with impaired hepatic and renal function, for which periodic monitoring of these two organs would be necessary.
The same care should be given to patients suffering from alterations of the haematological picture, for which the intake of mesalazine could coincide with severe blood dyscrasias.
The nature of the active ingredient and the presence of easily allergenic excipients can be responsible for allergic reactions, even severe ones, in hypersensitive patients, so it would be useful to stop therapy immediately.
The presence of lactose in ASACOL ® gastro-resistant tablets could be associated with the development of adverse reactions of the gastrointestinal tract in patients with glucose / galactose malabsorption or lactase enzyme deficiency.
Although the drug itself is not capable of altering the patient's perceptive abilities, some of its side effects, and in particular headache, could make the use of machinery and driving cars dangerous.
PREGNANCY AND BREASTFEEDING
The absence of clinical trials and significant studies regarding the use of Mesalazine during pregnancy and lactation and the related effects on the health of the fetus and infant, prevent the characterization of the safety profile of ASACOL ®
For this reason, taking this medicine should be discouraged during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Interactions
Although the low systemic absorption of mesalazine significantly reduces the risk of possible interactions, it is advisable to avoid the simultaneous intake of agents such as lactulose capable of lowering the pH of the intestinal lumen, delaying the release of mesalazine and drugs from the renal metabolism, in order to to reduce the risk of kidney disease.
The concomitant intake of corticosteroids, useful in the acute phases of the disease, could determine a significant increase in the anti-inflammatory potential of mesalazine.
Finally ASACOL ® could interact with active ingredients such as coumarins, methotrexate, probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, spironolactone, furosemide, rifampicin and sulfonylureas with not fully characterized effects.
Contraindications ASACOL ® Mesalazine
ASACOL ® is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the active substance or analogues belonging to the salicylate family, and in patients with lesions of the gastric and duodenal mucosa or severe nephropathies.
ASACOL ® is also contraindicated in children under 2 years of age and in women in the last weeks of pregnancy or in the breastfeeding period.
Undesirable Effects - Side Effects
The intake of mesalazine was found to be well tolerated and without clinically significant side effects.
The most commonly observed adverse reactions involved the gastrointestinal tract with nausea, diarrhea and abdominal pain and the nervous one with headache.
On several occasions, hypersensitivity symptoms were noted with rashes, itching, rash and fever for which it was necessary to quickly discontinue therapy.
Alterations in the haematological picture and in renal and hepatic function were decidedly rarer.
Note
ASACOL ® is a prescription drug.
The information on ASACOL ® Mesalazine published on this page may be out of date or incomplete. For a correct use of this information, see the Disclaimer and useful information page.